Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262, p.012035_1 - 012035_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.52(Physics, Applied)Using spin-polarized positrons, the excess spins in magnetic substances can be detected. For efficient measurements with spin-polarized positrons, a strong enough source emitting highly polarized positrons is needed. For this purpose, we focus on a  Ge radioisotope. This radioisotope decays to
Ge radioisotope. This radioisotope decays to  Ga with a half-life of 280 days. The endpoint positron energy is 1.9 MeV and hence the theoretical longitudinal spin polarization is approximately 94%. This radioisotope can be produced though the nuclear reaction of
Ga with a half-life of 280 days. The endpoint positron energy is 1.9 MeV and hence the theoretical longitudinal spin polarization is approximately 94%. This radioisotope can be produced though the nuclear reaction of 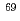 Ga (p,2n)
Ga (p,2n)  Ga. In this study, we report the production of
Ga. In this study, we report the production of  Ge by proton irradiation. We examined a metal form
Ge by proton irradiation. We examined a metal form 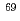 Ga stable isotope and a GaN substrate as target materials. When the metal
Ga stable isotope and a GaN substrate as target materials. When the metal 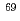 Ga targets were used, the production rates of
Ga targets were used, the production rates of  Ge were 0.16 and 0.14 MBq/
Ge were 0.16 and 0.14 MBq/ A/h for 20 and 25 MeV, respectively. Using the GaN target, it was 0.24 MBq/
A/h for 20 and 25 MeV, respectively. Using the GaN target, it was 0.24 MBq/ A/h. Thus,
A/h. Thus,  Ge radioisotopes were generated in both targets. The spin polarizations of positrons emitted from
Ge radioisotopes were generated in both targets. The spin polarizations of positrons emitted from  Ge and
Ge and  Na were estimated to be approximately 90% and 30%, respectively.
Na were estimated to be approximately 90% and 30%, respectively.
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Hasegawa, Shigehiko*; Zhou, Y. K.*; Asahi, Hajime*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262(1), p.012066_1 - 012066_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.06(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262, p.012067_1 - 012067_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.52(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Hori, Fuminobu*; Onodera, Naoto*; Fukumoto, Yuka*; Ishii, Akito*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Maekawa, Masaki; Yokoyama, Yoshihiko*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 262, p.012025_1 - 012025_4, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:84.8(Physics, Applied)Free volume changes in Zr Cu
Cu Al
Al bulk glassy alloys irradiated by 200 and 2.5 MeV Xe ions, 180 keV He ions, and 2 MeV electrons were investigated at room temperature using positron annihilation techniques. X-ray diffraction revealed that no crystallization took place in any of the irradiated sample. The positron lifetime increased only after electron and 180 keV He irradiation. This indicates that the radiation has increased the open volume size (free volume). On the other hand, the positron lifetime was decreased by irradiation with heavy Xe-ions at either energy of 2.5 or 200 MeV. It is conceivable that the difference in behavior can be attributed to the difference in displacements per radiation particle (dpp), because the dpp estimated for 2 MeV electrons and 180 keV He ions is three or more orders of magnitude less than that for heavy Xe ions. We found that the radiation effect in ZrCuAl bulk glassy alloy is dependent on the displacement per radiation particle.
bulk glassy alloys irradiated by 200 and 2.5 MeV Xe ions, 180 keV He ions, and 2 MeV electrons were investigated at room temperature using positron annihilation techniques. X-ray diffraction revealed that no crystallization took place in any of the irradiated sample. The positron lifetime increased only after electron and 180 keV He irradiation. This indicates that the radiation has increased the open volume size (free volume). On the other hand, the positron lifetime was decreased by irradiation with heavy Xe-ions at either energy of 2.5 or 200 MeV. It is conceivable that the difference in behavior can be attributed to the difference in displacements per radiation particle (dpp), because the dpp estimated for 2 MeV electrons and 180 keV He ions is three or more orders of magnitude less than that for heavy Xe ions. We found that the radiation effect in ZrCuAl bulk glassy alloy is dependent on the displacement per radiation particle.
Kawasuso, Atsuo; Maekawa, Masaki; Fukaya, Yuki; Yabuuchi, Atsushi; Mochizuki, Izumi
no journal, ,
We review on-going two research projects (Study of surface low-dimensional materials using reflection high-energy positron diffraction(RHEPD), Application of spin-polarized positron beam for magnetic substances) in JAEA. As for the former project, we introduce the principle of RHEPD, the energy-loss process in positrons and the metal-insulator transition of Si(111)-In surface. As for the latter project, we report the production of 68-Ge positron source, its spin polarization and the trial positron annihilation measurements of some magnetic substances.